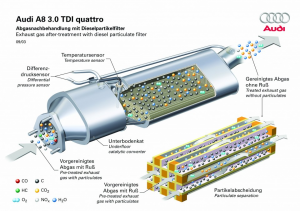
With the popularization of energy-saving and environmental protection concepts in the automotive industry, the global diesel particulate filter market has a good prospect. The particulate filter DPF (Diesel Particulate Filter) is a ceramic filter installed in the diesel engine exhaust system. traps material before it enters the atmosphere. DPF is made of porous wall-flow ceramic material and coated with precious metal coating, and is divided into four parts: package, clamp, carrier, and line

Since diesel engines are 30% more fuel-efficient than gasoline engines and have 30%-45% lower carbon dioxide emissions, dieselization has become an important development direction for the automotive industry. The application of diesel particulate filter (DPF) to solve diesel engine particulate matter and nitrogen oxide emissions has also received attention from various countries.

Diesel engines pollute mainly from three sources – particulate matter, hydrocarbons (HCx), nitrogen oxides (NOx) and sulfur. Among them, the particulate matter (soot) is mostly composed of tiny particles of carbon or carbide (size less than 4-20 μm).
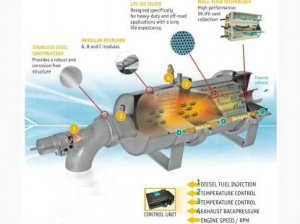
Its basic working principle is: if the diesel particulate filter is sprayed with metal platinum, laurium, and palladium, the black smoke containing carbon particles discharged from the diesel engine enters the engine exhaust particulate filter through a special pipeline, and passes through the densely arranged inside. The bag filter absorbs the soot particles on the filter made of metal fiber felt; when the adsorption amount of the particles reaches a certain level, the burner at the end automatically ignites and burns the soot particles adsorbed on it, into carbon dioxide that is harmless to the human body.
To do this, the catcher employs advanced electronic control systems, catalytic coatings and fuel-added catalysts (FBC). This fuel-added catalyst contains metals such as palladium, iron and platinum. These materials are added in proportion to the fuel, and with the help of the engine control system, not only the amount of particulate matter is controlled, but also the emission of pollutants such as hydrocarbons and polluting gases. The regeneration or purge function of the trap must be done on a controlled basis to keep the trap from becoming clogged with soot.
DPF regeneration: DPF burns the collected soot particles through exhaust heating. This process is called DPF regeneration. DPF is divided into passive regeneration and active regeneration: passive regeneration, carbon dioxide particles are oxidized at 250-450°C, NO is oxidized to NO2 in DOC, passive regeneration is always going on, just because the exhaust temperature is different, the speed of passive regeneration is different; active Regeneration: In actual operating conditions, the exhaust gas temperature does not meet the passive regeneration conditions. It is necessary to generate oxidation reaction in DOC through fuel injection to increase the exhaust temperature to above 550°C, so that carbon combustion and oxidation reactions generate carbon dioxide.
Hope it will be helpful for your side and please don’t hesitate to contact me if you need further information
Post time: Jan-09-2023